




Explore a thousand years of European history through pivotal events that defined the medieval world, from the fall of Rome to the dawn of the Renaissance.
The Middle Ages span nearly a millennium of European history, from the fall of the Western Roman Empire to the beginning of the Renaissance. This interactive timeline highlights key events that shaped this complex and fascinating period.



















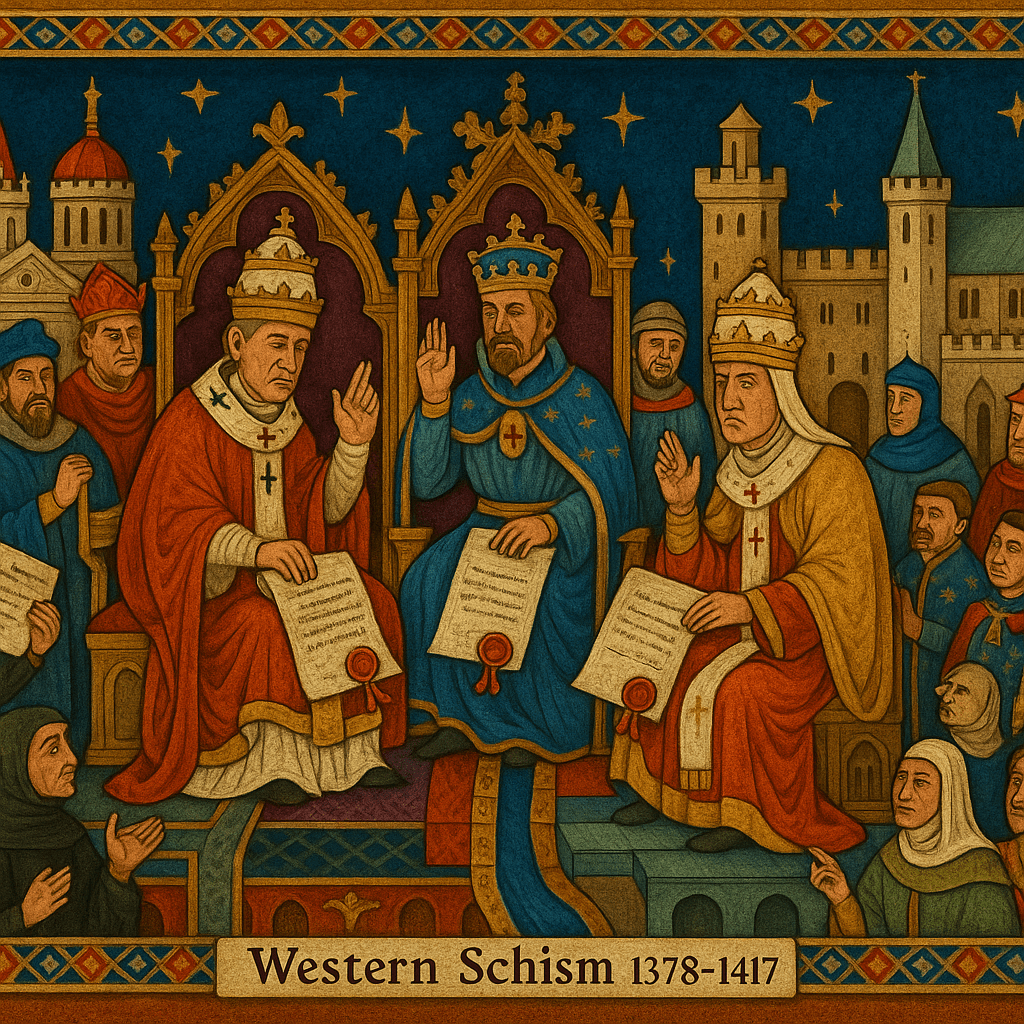
This timeline presents pivotal events that shaped the medieval period, a time of immense cultural, religious, and political transformation in Europe and beyond. The symbolic artwork accompanying each event aims to capture the deeper significance of these historical moments.
The Middle Ages saw the rise of feudalism, the growth of Christianity, the emergence of universities, the development of Gothic architecture, and countless other innovations that laid the groundwork for the modern world.
For those interested in exploring medieval history further, we recommend consulting academic sources, museums with medieval collections, and reliable online resources dedicated to this fascinating period.
Each event in our timeline includes a link to Wikipedia for initial exploration, but we encourage deeper research through books, documentaries, and scholarly articles to develop a more comprehensive understanding of this complex era.